[ad_1]
US researchers have designed a 2D photo voltaic cell primarily based on TMDCs that may far exceed the effectivity of this machine typology, which generally doesn’t exceed 6%. The innovation of this cell consists of the superlattice construction, which the analysis crew says can separate the 2D TMDC layers by a spacer, thus bettering mild absorption.
A gaggle of researchers from the College of Pennsylvania in america has designed a 2D photo voltaic cell primarily based on transition steel dichalcogenides (TMDCs) with a particular superlattice construction that’s reported to allow larger ranges of photo voltaic absorption.
TMDCs are two-dimensional supplies with distinctive semiconducting properties and excessive optical absorption coefficients, making them appropriate for the fabrication of semi-transparent and versatile photo voltaic cells with potential purposes in aerospace, structure, electrical autos, and wearable electronics, the place mild weight, excessive power-per- weight ratio, and suppleness is very fascinating. .
“I believe persons are slowly realizing that 2D TMDCs are superb photovoltaic supplies, even when not for terrestrial purposes, however for cellular purposes—extra versatile, like purposes that space-based,” mentioned lead creator Deep Jariwala. “The load of 2D TMDC photo voltaic cells is 100 instances lower than silicon or gallium arsenide photo voltaic cells, so all of a sudden these cells turn out to be a beautiful know-how.”
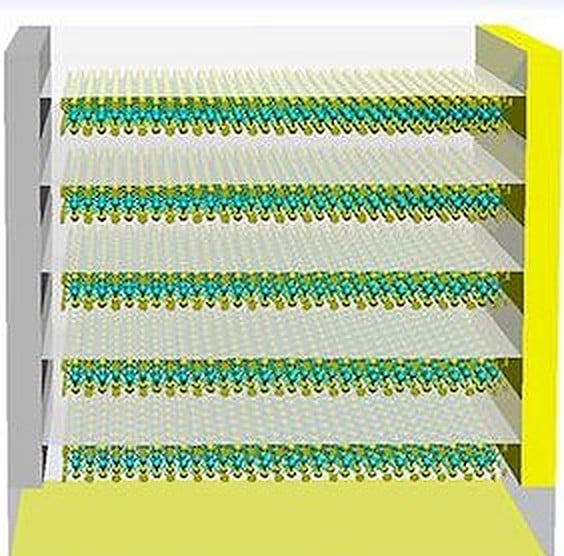
The scientists constructed the cell utilizing a monolayer absorber fabricated from molybdenum disulfide (MoS).2), a 3 nm insulator primarily based on aluminum oxide (Al2or3) positioned on a substrate fabricated from Al2or3 and gold (Au), with the latter performing as a reflector. “The thickness of Al2or3 layer has been optimized to reinforce photocarrier technology,” they defined. “The energetic layer of the machine is intrinsically 0.98 μm lengthy, with silver and gold cathode and anode electrodes measuring 0.01 μm lengthy every.”
Based on the researchers, the innovation of this cell consists of its superlattice construction, which they are saying can separate the layers of 2D TMDCs by a spacer or non-semiconductor layer. “The spacing of the layers lets you bounce mild many, many instances inside the cell construction, even when the cell construction may be very skinny,” Jariwala mentioned, noting that the cell reveals massive exciton binding energies.
When examined in a sequence of simulations, the proposed cell design with separate contacts was in a position to obtain an influence conversion effectivity of 12.87%. As a means of comparability, actual 2D TMDC photo voltaic cells far obtain efficiencies of as much as 6%.
“We do not count on cells which might be very skinny to see 12% worth. Provided that present efficiencies are lower than 5%, my hope is that within the subsequent 4 to five years folks will be capable of” g will present cells of 10% and above effectivity,” mentioned the researchers.
They describe the brand new cell know-how within the paper “How environment friendly are 2D excitonic photo voltaic cells?” printed in TOOLS. “Our findings present that 2D TMDC-based PVs, when optimized for optical and digital design, present superior efficiency in comparison with different thin-film supplies when it comes to energy density, which necessary for a lot of purposes comparable to aerospace, distant sensing, and wearable know-how,” they concluded.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
[ad_2]
Source link