Lithium Titanate vs Lithium-Ion Battery: In the world of modern energy storage, choosing the right battery technology is crucial. Two major contenders are Lithium Titanate (LTO) and conventional Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) batteries. While both serve similar purposes—powering electric vehicles, renewable storage, and backup systems—their underlying chemistry, performance, and applications differ significantly.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into lithium titanate vs lithium-ion, explaining their characteristics, advantages, drawbacks, and ideal use cases. Whether you’re a buyer, engineer, or consultant, this guide will help you make informed decisions.
🔬 What Is a Lithium-Ion Battery?
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable energy storage systems that use graphite for the anode, lithium metal oxide (like NMC, LFP, or LCO) for the cathode, and a liquid electrolyte to carry lithium ions during charging and discharging.
Key Characteristics:
- High energy density
- Moderate cost
- Good power output
- Common in smartphones, EVs, and solar batteries
🔬 What Is a Lithium Titanate Battery (LTO)?
Lithium Titanate (LTO) batteries are a type of lithium-ion battery, but instead of graphite, they use lithium titanate (Li₄Ti₅O₁₂) as the anode material. The cathode can still be NMC or another lithium metal oxide.
Key Characteristics:
- Ultra-fast charging
- Extremely long cycle life
- Superior safety
- Lower energy density
⚖️ Lithium Titanate vs Lithium-Ion: Full Comparison Table
| Feature | Lithium-Ion Battery (Li-ion) | Lithium Titanate Battery (LTO) |
|---|---|---|
| Anode Material | Graphite | Lithium Titanate |
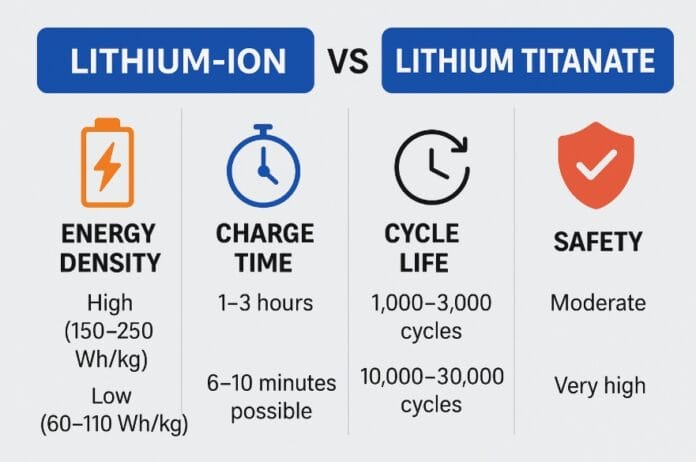
| Energy Density | High (150–250 Wh/kg) | Low (60–110 Wh/kg) |
| Charge Time | 1–3 hours | 6–10 minutes possible |
| Cycle Life | 1,000–3,000 cycles | 10,000–30,000 cycles |
| Operating Temp. | 0°C to 45°C | -30°C to 55°C |
| Charging Safety | Moderate (risk of thermal) | Very safe (stable structure) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Self-Discharge | Moderate | Very Low |
| Applications | EVs, phones, ESS | Buses, military, aerospace, UPS |
🔋 1. Energy Density
Li-ion wins here.
Lithium-ion batteries have much higher energy density—meaning they can store more energy per kg or liter. That’s why they’re preferred for:
- Electric cars that need long range (like Tesla)
- Mobile phones and laptops
LTO, on the other hand, has a lower energy density, which makes it bulky for the same amount of power. This limits its use in compact devices.
⚡ 2. Charging Time
LTO takes the lead.
Lithium titanate batteries can be charged to 80% in just 6-10 minutes. The fast lithium-ion movement in titanate anodes allows ultra-fast charging without overheating.
Li-ion batteries usually take 1 to 3 hours, and fast charging often degrades them over time.
🔁 3. Cycle Life
This is a game-changer for LTO.
Lithium-ion batteries offer around 1,000 to 3,000 cycles depending on quality and chemistry (NMC, LFP, etc.). LTO batteries can last 10,000 to 30,000 cycles, making them ideal for:
- Long-term investments
- Industrial and utility-scale energy storage
- Heavy-use applications
🌡️ 4. Temperature Performance
LTO works better in extreme climates.
LTO batteries can operate from -30°C to 55°C, whereas standard lithium-ion batteries work best between 0°C and 45°C.
This makes LTO suitable for:
- Arctic military deployments
- Hot and dusty industrial zones
- Outdoor ESS systems
🔥 5. Safety
LTO is much safer.
Its stable lithium titanate anode prevents dendrite formation, a common issue in Li-ion batteries that can cause thermal runaway and fire. LTO is non-flammable, even under short-circuit or overcharge conditions.
Li-ion requires extra BMS safety layers to avoid overheating.
💰 6. Cost
Li-ion wins in affordability.
Lithium-ion batteries are cheaper per Wh, making them the economical choice for:
- Consumer electronics
- Budget EVs
- Solar home systems
LTO batteries can be 2 to 4 times more expensive, but the cost may be justified in high-use scenarios due to longevity and safety.
🔋 7. Self-Discharge and Storage
LTO has extremely low self-discharge.
You can leave an LTO battery for months without major energy loss. Li-ion cells self-discharge faster and degrade more over time, especially in high temperatures.
🚚 8. Applications Comparison
Where Lithium-Ion Is Preferred:
- Smartphones and laptops
- Electric vehicles (Tesla, BYD)
- Residential solar battery storage
- Power tools
Where LTO Is Preferred:
- Rapid charging stations
- Electric buses and trains
- Military-grade energy systems
- UPS for data centers and hospitals
- Space and aerospace missions
- Cold climate backup systems
✅ Pros and Cons Summary
✅ Pros of Lithium-Ion:
- Higher energy density
- Cheaper
- Widely available
- Lighter weight
❌ Cons of Lithium-Ion:
- Lower cycle life
- Risk of fire or thermal events
- Degrades faster at high temperatures
✅ Pros of Lithium Titanate:
- Ultra-long life (up to 30,000 cycles)
- Very fast charging
- Excellent temperature tolerance
- Extremely safe and stable
❌ Cons of Lithium Titanate:
- Low energy density
- Higher cost
- Bulkier size
🤔 Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between lithium titanate vs lithium-ion depends on your specific needs:
| If You Need… | Go With… |
|---|---|
| High energy storage in a small size | Lithium-ion |
| Low cost and mass adoption | Lithium-ion |
| Long lifespan and ultra-fast charging | Lithium Titanate |
| Extreme safety and temperature range | Lithium Titanate |
| Industrial or military-grade usage | Lithium Titanate |
📌 Real-World Use Case Example
🚗 Electric Buses:
LTO is used in many China-based electric buses, such as those in the city of Shenzhen. They recharge in under 10 minutes and run reliably all day.
⚡ Home ESS:
🙋♂️ FAQs
Q1: Is LTO better than Li-ion?
It depends on the application. LTO is better for safety, life, and speed. Li-ion is better for compact energy storage.
Q2: Why is LTO not used in mobile phones?
Because of its low energy density and higher cost. It would make phones bulky and expensive.
Q3: Are LTO batteries safe?
Yes. They are one of the safest battery chemistries available, with virtually no fire or explosion risk.
🧠 Final Thoughts
Both lithium titanate and lithium-ion batteries have their own strengths and ideal use cases. If you’re looking for compact, cost-effective solutions, lithium-ion is your go-to. But if your project demands ultra-fast charging, extreme safety, and long life, LTO is worth the premium.
Make your decision based on what matters most to your application—whether it’s size, cost, longevity, or safety.
📌 Need help sourcing LTO or Li-ion batteries for your project?
With over 13 years in China’s new energy industry, I help clients globally source reliable, tested, and certified battery systems. Feel free to connect with me on LinkedIn