[ad_1]
Prototype Ca steel battery
Picture: Tohoku College, Inventive Commons License CC BY 4.0
Rechargeable calcium steel batteries have emerged as a promising possibility within the seek for next-generation vitality storage units, that are anticipated to have increased vitality densities and decrease prices than present ones. lithium-ion batteries. Nonetheless, challenges, akin to calcium steel passivation by electrolytes and lack of cathode supplies with environment friendly calcium ion storage capabilities, hinder the sensible growth of the know-how.
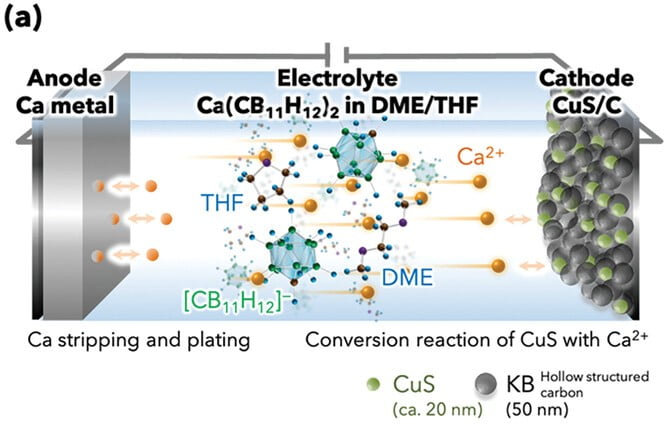
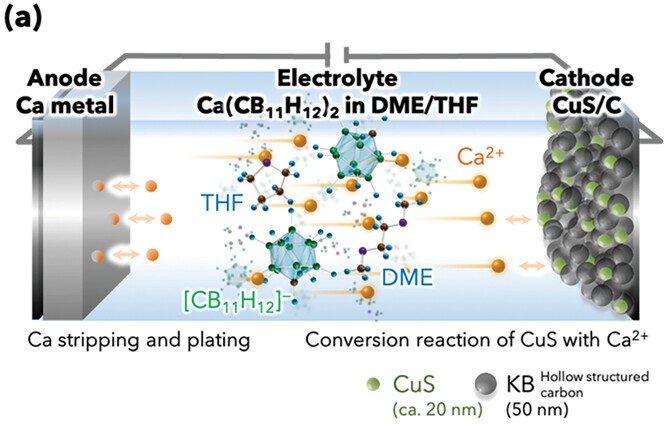
To beat these limitations, researchers at Tohoku College in Japan have not too long ago developed a prototype calcium steel rechargeable battery that may carry out greater than 500 cycles of repeated charging and discharging. The battery was developed utilizing a hydride-based electrolyte and a copper sulfide (CuS) nanoparticle/carbon composite cathode. It exhibits higher efficiency than state-of-the-art calcium steel batteries by way of fee functionality and cycle life.
The mix of a CuS/C nanocomposite and a tailor-made monocarborane electrolyte resolution of Ca(CB11H12)2 of dimethoxyethane/tetrahydrofuran (DME/THF) enabled a calcium steel battery with a capability retention of 92% primarily based on the capability of the tenth cycle.
“This research confirms the opportunity of long-term operation of Ca steel anodes and might speed up the event of Ca steel batteries,” the researchers wrote in “Calcium Steel Batteries with Lengthy Life Utilizing Hydride-Based mostly Electrolyte and Copper Sulfide Electrode ,” which was not too long ago printed in Superior Science.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
[ad_2]
Source link