[ad_1]
Researchers at IIT Mandi have developed high-quality, uniform skinny movies of nickel oxide on a silicon substrate utilizing an aerosol-assisted chemical vapor deposition method, with nickel nitrate because the precursor materials.
From pv journal India
Extremely selective contacts are the important thing to reaching excessive effectivity in skinny movie photo voltaic cells. These contacts enable one kind of provider (holes) to conduct and block different sorts (electrons).
Nickel oxide (NiO) is a wonderful materials for hole-selective contacts and is broadly utilized in many PV applied sciences. Nickel oxide movies with thicknesses within the nanometer vary (100 thousand occasions smaller than the width of a human hair) should be produced to be used in advanced-architecture silicon photo voltaic cells.
Nonetheless, the present technique of growing nanometric skinny nickel oxide membranes by sputtering may be very costly as a result of the gear used to provide it should be imported. Fundamental components like nickel acetylacetonate used to develop these membranes are very costly. The price of this system limits the probabilities of its use.
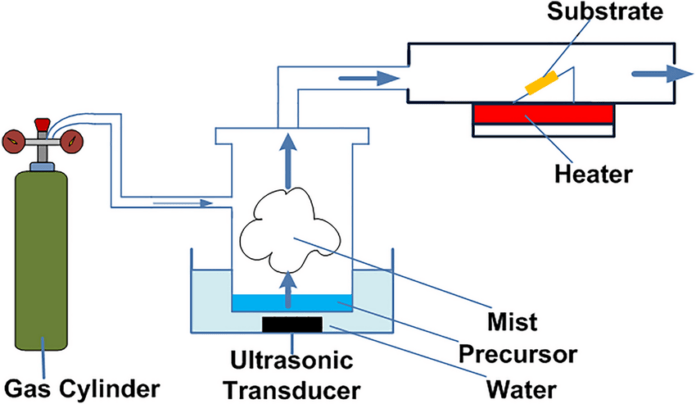
Researchers on the Indian Institute of Expertise Mandi (IIT Mandi) have developed a low-cost course of to create ultra-thin movies of steel oxides from cheaper beginning supplies. Particularly, they used an aerosol-assisted chemical vapor deposition method to deposit a nickel oxide skinny movie on a silicon substrate.
“The aerosol-assisted chemical vapor deposition method can produce high-quality, uniform skinny movies on a wide range of surfaces, together with silicon, by delivering a vapor section precursor within the type of an aerosol,” mentioned the researcher. Kunal Ghosh, who led the examine. “Aerosol permits the deposition of a variety of oxide-based supplies with excessive precision, making it a flexible and efficient methodology for varied functions in supplies science and engineering:”
The group used nickel nitrate hexahydrate because the nickel salt and the deposition was carried out at 550 C for a interval of quarter-hour to provide nickel oxide movies with a thickness of roughly 15 nanometers. They analyzed the morphology and composition of nickel oxide movies produced utilizing totally different detection methods.
The undertaking remains to be within the early phases of growth. Nonetheless, the expertise has the potential to be adopted by the business. This analysis will enhance the manufacturing technique of superior structure silicon photovoltaic units, decreasing the associated fee and complexity of economic methods.
“Our analysis reveals that it’s potential to develop a cheap and scalable course of for the manufacturing of steel oxide layers for photo voltaic cells,” mentioned Ghosh. “This new methodology has the potential to revolutionize the photo voltaic business by decreasing the associated fee and complexity of present manufacturing methods. As well as, as your entire course of together with the gear is finished in-house, the which IP will contribute to India’s self-reliance within the space of advanced-architecture silicon photo voltaic cells.
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
[ad_2]
Source link