[ad_1]
Researchers in Egypt have developed a novel gap transport layer (HTL) for inverted perovskite photo voltaic cells utilizing silver thiocyanate as an alternative of the generally used PEDOT: PSS and copper thiocyanate. The brand new HTL materials reveals distinctive effectivity and sturdiness within the constructed cell.
Researchers from the Central Metallurgical Analysis and Growth Institute (CMRDI) in Egypt have produced an inverted perovskite photo voltaic cell with a brand new sort of gap transport layer (HTM) primarily based on silver thiocyanate (AgSCN). Scientists intention to interchange generally used gap transport supplies equivalent to PEDOT:PSS and copper thiocyanate (CuSCN) with AgSCN.
“Some great benefits of CuSCN lie in the truth that it will possibly function a gap transport layer and a supply of Cu doping, whereas AgSCN, with its better resistivity, can function a supply of Ag doping with slower diffusion fee,” the scientists. defined, noting that AsSCN can also be higher at transferring costs between the HTL and perovskite layer in comparison with PEDOT:PSS.
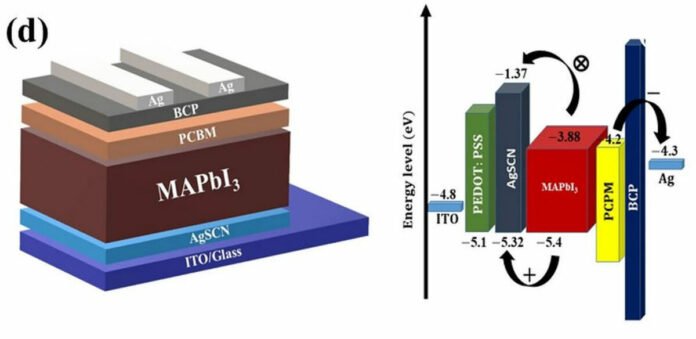
The group constructed the cell with an indium tin oxide (ITO) substrate, a electron transport layer (ETL) primarily based on AgSCN, an absorber primarily based on a sort of lead-halide perovskite generally known as methylammonium lead iodide (MAPbI3), a phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM) layer, a bathocuproine (BCP) buffer layer, and a silver (Ag) steel contact.
The lecturers deposited the skinny movie of AgSCN in a dry glove field with a relative humidity between 25% and 30% not less than half-hour earlier than beginning the deposition of the perovskite layer. Then they deposited the perovskite layer on the HTL energetic layer by spin coating at 4,000 rpm for 30 seconds. The efficiency of the photo voltaic cell is in contrast with a reference machine made utilizing HTM primarily based on PEDOT:PSS.
The AgSCN-based machine achieved an influence conversion effectivity of 16.66%, an open-circuit voltage of 1.14 mV, a short-circuit present of 19.0 mA/cm2, and a fill issue of 77.1%. The PEDOT:PSS cell reached an effectivity of 15.11%, an open-circuit voltage of 1.04 V, a short-circuit present of 18.17 mA/cm2, and a fill issue of 80.37%.
“The efficiently achieved skinny movie of AgSCN produced a greater perovskite movie with free pinholes and enormous grains, whereas the skinny movie of PEDOT:PSS produced the same high quality perovskite movie with pinholes found,” the crew defined, noting that the AgSCN cell was additionally capable of retain 80.9% of its preliminary effectivity after 500 hours in an environment with 48% relative humidity.
“This low-temperature, low-cost manufacturing technique of AgSCN is discovered to be simple and scalable, which is sweet for the commercialization of perovskite-based versatile units and photovoltaic applied sciences,” the researchers concluded. “Basically, AgSCN is a non-toxic, low-cost different that’s easy to make use of at low temperatures. It’s a robust contender for the manufacturing of tandem units and high-efficiency pin junction photo voltaic cells that product of perovskites.
They describe the cell tech in “AgSCN as a brand new hole-carrying materials for inverted perovskite photo voltaic cells,” just lately printed in Scientific reviews.
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
[ad_2]
Source link