[ad_1]
A Bangla-Japanese analysis crew has constructed a copper silver bismuth iodide (CABI) PV system utilizing an unexplored CABI compound. The scientists utilized a blended solvent-based hot-casting approach to enhance the floor morphology of the CABI movie and enhance cell effectivity.
A global analysis crew created a copper silver bismuth iodide (CABI) photo voltaic cell that makes use of Cu6AgBiI10a brand new CABI compound that provides excessive absorption and low reflectivity.
“The development of photo voltaic cells primarily based on CABI just isn’t new,” the corresponding writer of the analysis, Arif Ul Islam, mentioned. pv journalIt’s famous that the earlier two makes an attempt made to develop this cell know-how had been primarily based on CABI supplies often known as CuAgBiI5 and Cu2AgBiI6, leading to efficiencies of 1.01% and a pair of.39%, respectively. “Our work, nonetheless, represents the primary try to create a photo voltaic cell primarily based on Cu6AgBiI10which is a specific sort of CABI materials.”
The scientists utilized a blended solvent-based hot-casting approach to enhance the floor morphology of Cu6AgBiI10 movie, which they are saying is meant to attain the very best potential photovoltaic performances. They use a one-step spin coating approach, the place scorching droplets are dropped onto preheated substrates.
“The answer was painted at 3000 rpm for 30 seconds,” they defined, including that the thickness of the CABI movies diverse between 1183 and 1506 nm. “The movies are then annealed within the glovebox at 75 C for 3 minutes after which heated at totally different temperatures (130 to 170 °C) for six minutes on a hot-plate. The movies are then allowed to chill naturally to ambient temperature.”
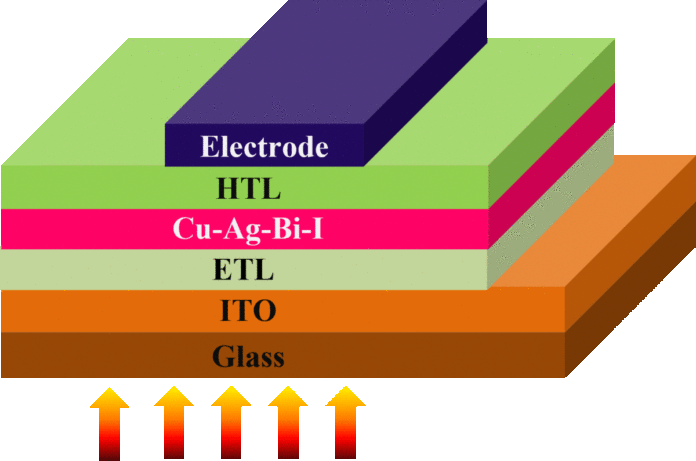
The movie is used as an absorber in a PV system fabricated from a substrate fabricated from indium tin oxide (ITO) and glass, an electron transport layer (ETL) primarily based on tin(IV) oxide (SnO).2), the absorber itself, is a gap transport layer (HTL) dependent the polymer Regioregular poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT), and a silver (Ag) metallic contact.
The analysis crew analyzed the optical traits of the cell and located that it might obtain an influence conversion effectivity of 0.041% and a most present density of 0.45 mA/cm.2, at ambient circumstances. “Our optical investigation revealed excessive absorbance and low reflectivity CABI movie at 150 C,” it additionally mentioned.
“Bismuth is discovered abundantly within the earth’s crust, which makes it cost-effective,” Islam emphasised. “Our outcomes ought to assist to develop environment-friendly Cu-Ag-Bi-I primarily based photo voltaic cells, in addition to a wide range of different units equivalent to photodetectors or LEDs.”
The photo voltaic cell structure is introduced within the paper “Improved floor morphology and photovoltaic properties of a brand new sort of Copper Silver Bismuth Iodide Photo voltaic Cell materials,” printed in Journal of Supplies Analysis and Know-how. The analysis crew consists of scientists from the College of Barishal in Bangladesh and the Nagoya Institute of Know-how in Japan.
This content material is protected by copyright and will not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
[ad_2]
Source link