[ad_1]
Scientists in Belgium have designed a solar-powered electrolyzer that makes use of standard-sized, large-area shingled silicon PV for water splitting. The system is reported to be able to reaching solar-to-hydrogen effectivity of 10% at electrolyzer present densities of roughly 60 mA cm−2.
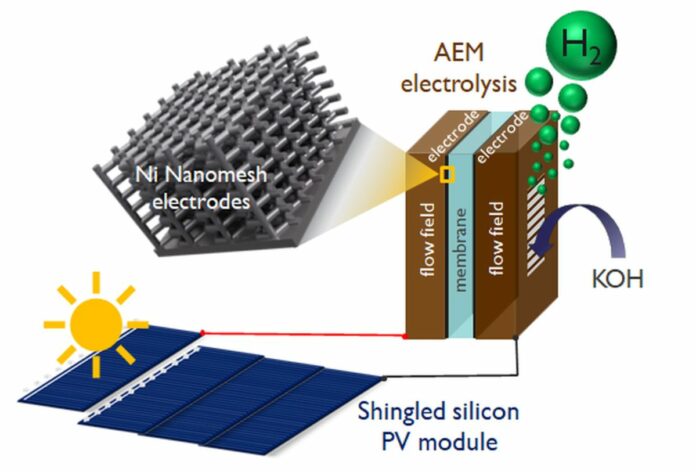
Researchers at Imec in Belgium have developed an anion trade membrane (AEM) electrolysis of water for hydrogen era. They are saying their methodology may be mixed with photo voltaic era in a photovoltaic-electrolyzer (PV-EC) configuration.
“The innovation of our method consists of utilizing standard-sized large-area shingled silicon PV to offer over 1.23V for water splitting mixed with low-cost anion-exchange water electrolysis, which mixes the upper densities of the present operation of the polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) with low cost supplies from alkaline electrolysis,” mentioned researcher Nina Plankensteiner pv journal.
The scientists introduced their findings in “Photovoltaic-Electrolyzer System Working at >50 mA cm-2 by Combining Giant-Space Shingled Silicon Photovoltaic Modules with Excessive Floor Space Nickel Electrodes for Low-Price Inexperienced H2 Era,” which was lately revealed in RRL Photo voltaic. They defined that PV-ECs provide the very best stage of know-how readiness and highest solar-to-hydrogen efficiencies of all electrolyzer applied sciences.
“In PV-EC techniques the photovoltaic know-how of alternative, which commercially delivers low cost electrical energy with a secure effectivity of 20-25% at 30-40mA/cm2, are in-series linked silicon photo voltaic cells, which offer > 1.23V for water splitting,” says researcher Joachim John. “Within the subsequent decade, silicon-tandem configurations with perovskite top-cells might play an extra function in conversion efficiencies of round 30%.”
They describe the proposed system as having a “commercially related configuration.” They mentioned that the AEM electrolyzer has nanomesh electrodes with a big floor space of 26 m2/cm3 product of nickel-rich soil, as beforehand reported by researchers.
“The in-series shingling of silicon photo voltaic cells is a really enticing methodology for photo voltaic water splitting functions, as a result of a sufficiently excessive voltage per commonplace cell space may be achieved,” they are saying, in reference to shingled panels.
The modules haven’t any busbar constructions, with solely a small a part of the cells not uncovered to the solar. The cells are sure to type a shingled high-density string and the ensuing strips are linked by a conductive adhesive. Lowering the variety of busbars reduces shadow losses.
The lab-scale, single-cell electrolyzer developed by lecturers has two 4-micrometer skinny high-surface space nickel nanomesh electrodes. It additionally options six silicon heterojunction cells with shingles of 38.5 cm2 minimize from 15.6 cm2 x 15.6 cm2 commonplace cells.
“The cells are linked in collection and supply a variable open-circuit voltage vary from 0.7V to 4.3V, relying on the variety of cells linked,” the scientists defined, noting that the cells achieves a mean effectivity of round 20% and a fill issue of roughly 80%. “The present-voltage traits from the electrolyzer present that 1.8 V to 2.2 V is required to match an electrolyzer present density between 20 and 100mA/cm2. This minimal voltage requirement may be achieved by connecting three or 4 silicon cells in-series.
Examined below commonplace lighting situations, the PV-EC system was reported to provide hydrogen in about 20 hours and achieved a solar-to-hydrogen effectivity of 10% on the electrolyzer present density. which is roughly 60 mA cm-2which the workforce described as the very best density reported for PV-EC techniques within the literature.
Photo voltaic-to-hydrogen effectivity is set by in-situ monitoring of an important system parameters, resembling working present, voltage, and hydrogen gasoline move. The researchers say that the correct willpower of this determine of benefit is essential when evaluating PV-EC techniques to one another. They notice that greater stability measurements must be examined at excessive sufficient present densities to emphasize the system.
The researchers additionally performed a collection of efficiency dynamic load checks with gradual and sudden adjustments in energy enter throughout half a 12 months of photo voltaic radiation. They declare that checks present that cell voltage adjustments are small and have little affect on PV-EC operation and hydrogen manufacturing.
“The following steps in direction of the commercialization of the introduced PV-EC system are long-term out of doors stability checks along with greater load measurement protocols,” they concluded.
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
[ad_2]
Source link