[ad_1]
A sequence of fires that occurred between 2017 and 2019 introduced South Korea’s vitality storage market to a standstill. New analysis seeks at this time to make clear all of the causes of accidents and analyze the various social components that may trigger the continued prevalence of accidents.
A sequence of 28 consecutive battery fires that occurred in South Korea between 2017 and 2019 led the nation’s vitality storage market to finish paralysis.
The nation’s Ministry of Commerce, Trade and Power (MOTIE) reached some broad conclusions in its investigative report on the accidents. By taking methods aside and analyzing elements, it recognized many potential manufacturing defects and decided that some methods possible lacked satisfactory safety towards electrical shock. It additionally makes use of moisture, mud, and salt mist exams to determine environmental administration weaknesses in battery methods.
As well as, MOTIE highlights the difficulty of poor set up strategies and finds issues that may come up when installers mix vitality administration and management system elements from totally different producer – even when such elements usually are not designed for use as components of an built-in system.
These components, nevertheless, might not be all the explanations behind accidents, in response to new analysis from the Ulsan Nationwide Institute of Science and Know-how (UNIST) in South Korea. “Amua The research considers the influence and dangers related to social components related to battery fires, which have not often been thought of in earlier research,” the lead writer of the analysis, Ji-bum Chung, stated pv journal. “Though the chance of fireside is mitigated by the event of battery storage expertise, there are potential dangers corresponding to human error and regular accidents that may trigger folks, organizations, and social contexts through which the expertise.
In keeping with Chung, fires in Korea are socially constructed by way of environmental components corresponding to sturdy incentives, inadequate regulation, the totally different cultural backgrounds of stakeholders, the tight coupling of various sub-technologies and miscommunication, the systematic strain to hunt revenue. , and false sense of safety.
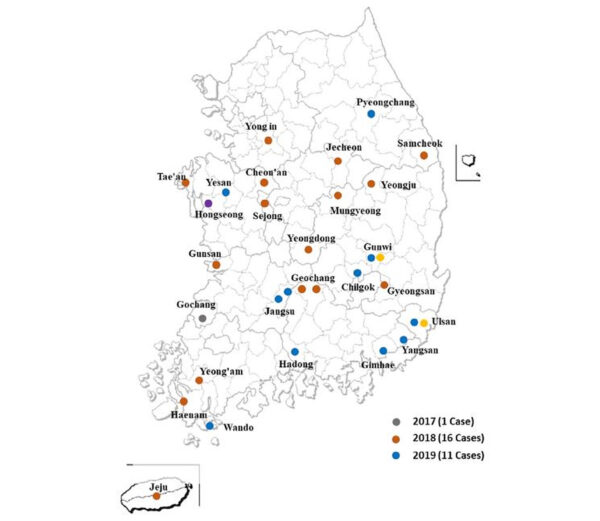
Picture: Ulsan Nationwide Institute of Science and Know-how
“These social components affect the prevalence of related social teams’ (RSGs) unfavorable interactions and result in unfavorable penalties such because the normalization of deviance and the hiddenness of the construction that accumulates in hearth hazards,” Chung additional defined. “Battery storage, an artifact created by social expertise, is seen negatively by these teams on account of a sequence of unintentional fires. In consequence, in 2021, the Korean authorities modified its insurance policies on storage from unusually sturdy assist to zero assist. The chilly perspective of the federal government led to the deterioration of the profitability of batteries that acted as an impediment to the event of the business, together with the chance of fireside.
on paper”The social development of fireside accidents in battery vitality storage methods in Korea,” just lately printed in Journal of Power Conservation, Chung and his colleagues introduced the outcomes of 24 interviews carried out in 2021 geared toward accumulating totally different interpretations of stakeholders on the causes of battery fires, together with members who participated in two official investigation committee established by MOTIE.
“Semantic Community Evaluation (SNA) and Thematic Evaluation (TA) had been carried out on all textualized interview information to look at key points,” the researchers defined. “Throughout the interviews, we discovered that social components, corresponding to insurance policies, laws, and organizational traits, are thought of an affect on battery hearth dangers.”
Additionally they used the social development of expertise (SCOT) principle to research the method of battery storage expertise development. This principle states that Know-how doesn’t decide human motion, however moderately, human motion shapes expertise.
The group concluded that RGSs don’t totally perceive the benefits and dangers of storage expertise and examine batteries as a strategy to keep financial incentives. “Such reckless use of expertise and lack of danger consciousness are motivations to forestall future technological dangers,” it stated. “Acceptable dangers could trigger members to make irrational selections based mostly on their pursuits. If a battery is abused, the chance of thermal runaway will increase. “
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
[ad_2]
Source link



