[ad_1]
US scientists have utilized the bandgap gradient to a cadmium telluride PV cell for the primary time. The result’s an enchancment in its effectivity and open-circuit voltage, and low non-radiative recombination.
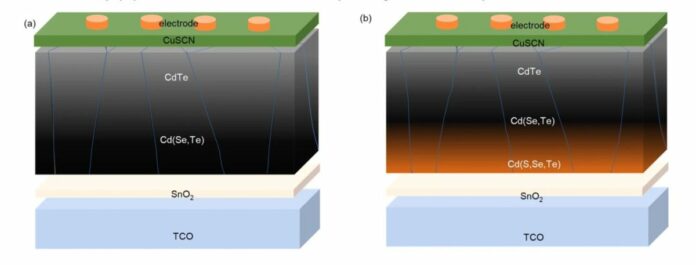
Researchers from the College of Toledo and the US Division of Power’s Oak Ridge Nationwide Laboratory have used a bandgap gradient for the primary time to enhance the efficiency of cadmium selenium telluride (CdSeTe) photo voltaic cells based mostly on business Tin(IV) oxide (SnO). .2) buffer layer.
The scientists describe their findings in “20%-efficient polycrystalline Cd (Se, Te) thin-film photo voltaic cells with a compositional gradient close to the entrance junction,” printed in Communication in Nature. They are saying that the business SnO2 The buffers are very secure and simply reproducible with the specified electron conductivity.
“Benefit from these benefits, SnO2 efficiently used for many years within the manufacturing of CdTe,” they are saying, noting that this buffer tech has just lately been changed by zinc magnesium oxide (ZMO). “The main impediment is the low electron conductivity of the ZMO buffer, which is troublesome to enhance even with extrinsic doping.”
The US workforce mentioned that the bandgap gradient has been efficiently utilized in different varieties of thin-film photo voltaic cells with the purpose of enhancing their open-circuit voltage, including that it needs to be utilized in CdSeTe units by incorporating a skinny layer of cadmium sulfide (CdS). within the entrance junction area whereas avoiding the formation of a damaging interface.
“The important thing to this success was the inclusion of oxygenated CdS and CdSe layers previous to the deposition of the CdTe absorber layer,” they mentioned.
The lecturers constructed the cell with a clear conductive oxide (TCO) layer, a SnO2 buffer layer, the above-mentioned oxygenated CdS and CdSe layers, a CdTe layer, and a copper(I) thiocyanate (CuSCN) gap extraction layer.
Examined below commonplace lighting circumstances, the machine achieved an influence conversion effectivity of 20.03%, an open-circuit voltage of 0.863 V, a short-circuit present of 29.2 mA cm-2, and a filling manufacturing facility at 79.5%. A reference cell constructed with no bandgap gradient reveals an effectivity of 18.3%, an open-circuit voltage of 0.834 V, a short-circuit present of 28.9 mA cm-2and a fill issue of 76.1%.
“We exhibit a technique to efficiently introduce a bandgap gradient penternary Cd area in Cd(Se,Te) photo voltaic cells with out the formation of a photo-inactive layer and a damaging hetero interface,” the scientists mentioned. “Decreased nonradiative recombination confirmed by time-resolved photoluminescence (TRPL) and photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) measurements.”
This content material is protected by copyright and will not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
[ad_2]
Source link