Researchers at Henan College in China have developed a perovskite photo voltaic cell primarily based on a carbon electrode that reportedly achieves an influence conversion effectivity of 20.8% whereas offering elevated stability.
The steel contact electrodes generally used immediately can stimulate the degradation of perovskite photo voltaic cells because of the diffusion of steel impurities on the interfaces. This problem can theoretically be overcome by changing the steel contact with carbon electrodes, that are very promising for commercialization because of their ambient stress processability primarily based on industrially established printing methods.
Perovskite photo voltaic cells primarily based on carbon electrodes, nevertheless, create issues elsewhere within the machine, resulting in a lack of efficiency on the level the place the carbon electrode meets the perovskite layer.
“For carbon electrode perovskite photo voltaic cells, the interfacial contact between the carbon electrode and perovskite is of nice significance to the efficiency of photo voltaic cells,” mentioned the scientists. “Most inorganic gap transport layers (HTLs) are primarily based on dispersive nanoparticles that simply combination to type poor contact with the perovskite and the viscous carbon paste; the gathering of holes is thus negatively affected.”
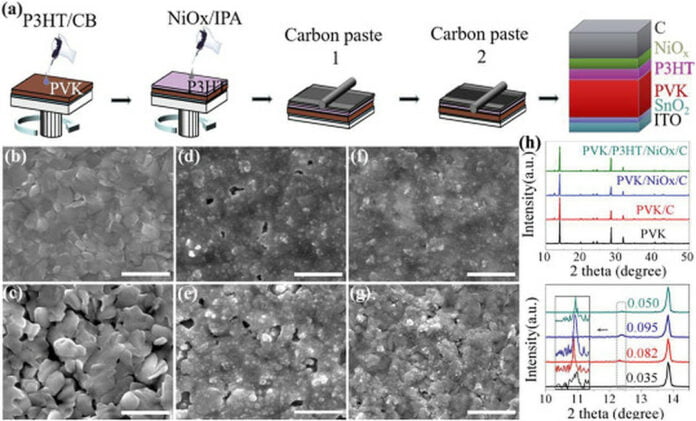
They sought to unravel this problem by putting an natural semiconducting polymer known as polythiophene (P3HT) between the perovskite and an HTL manufactured from nickel (II) oxide (NiOx) and mentioned that this natural/inorganic planar which HTL construction has the very best electrical contact for carbon electrode perovskite photo voltaic. cells.
“The natural P3HT layer permits efficient moisture-inhabitation and a densely contacted interface with a corresponding energy-level alignment with the perovskite, whereas the steady NiOx nanoparticle layer additional protects the P3HT from the degradation of the carbon paste in order that we are able to -optimize the carbon blade-coating deposition within the type densely contact with HTL,” in addition they defined.
The Chinese language group constructed the cell utilizing a substrate manufactured from indium tin oxide (ITO), a buffer layer of tin(IV) oxide (SnO2), a perovskite absorber, the P3HT layer, the HTL manufactured from NiOx, and a carbon electrode.
The electrode is predicated on a carbon paste containing carbon black and graphite powder offered by Saidi Know-how Growth Inc., China. “The carbon electrode is ready by the blade-coating course of and the moist movie is annealed at 110 C for five min,” it mentioned.
The lecturers in contrast the photo voltaic cell’s efficiency to a reference machine with out the modified anode buffer interface, which they are saying hastens cost assortment.
The champion photo voltaic cell constructed with these interfaces achieved an influence conversion effectivity of 20.8%, an open-circuit voltage of 1.15 eV, a short-circuit present of twenty-two.9 mA/cm2 , and a filling issue of 78.8%.
“This effectivity is among the highest values in carbon electrode perovskite photo voltaic cells; a champion effectivity of twenty-two% has been reported from the meeting of semi-cells with a carbon electrode substrate,” they mentioned. “The soundness of the operation of this cell is clearly improved because of an introduction of the hydrophobic P3HT layer and the dense carbon pre-covering.”
The reference machine, quite the opposite, reached an effectivity of solely 13.4%.