[ad_1]

In a security audit of greater than 600 rooftop PV programs, CEA discovered that 97% of installations had main security considerations. The engineering providers firm conducts inspections in the US, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, India, Japan, United Arab Emirates, Australia, Canada, Mexico, Czech Republic, Germany, Poland, and France.
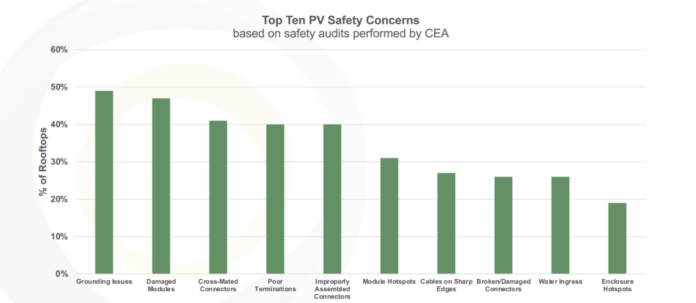
It shares the primary audit leads to a brand new report that identifies the highest 10 commonest security issues in audited programs. It’s mentioned that 49% of websites have grounding points, 47% have broken modules, 41% have cross-mated connectors, 40% have poor terminations and improper meeting of connectors, 31 % have module hotspots, 27% have cables on sharp edges, 26% have damaged or broken connectors in addition to water ingress, and 19% have enclosure hotpots.
“Most of those hazards are attributable to poor set up practices,” an organization spokesperson mentioned. pv journal. “This implies most of them will be rapidly recognized and resolved earlier than they result in fires, security hazards, and doubtlessly pricey liabilities.”
CEA found that the majority grounding points happen on the inverter or gear pad, between PV array blocks and module rows, and alongside prolonged entry paths, addressing the commonest security considerations. It additionally discovered that injury to modules is commonly attributable to incorrect set up or cleansing procedures, together with strolling on modules, in addition to excessive climate occasions similar to hail or wind.
CEA says websites exhibiting cross-mated connectors are sometimes the results of misunderstanding UL-listed connector pairings and the usage of field-made connectors that do not match the module connector.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].
[ad_2]
Source link