Researchers on the College of Hong Kong have found a sequence of anionic community stable electrolytes that may present a minimum of a fourfold enchancment in cationic transport for lithium-metal battery purposes.
Whereas lithium metallic batteries provide higher security, higher vitality density, and decrease weight than lithium-ion know-how – because of changing heavier graphite with lithium metallic because the anode – this battery chemistry doesn’t work properly with standard electrolytes.
Subsequently, analysis efforts are directed in direction of stable electrolytes that present higher efficiency and are appropriate with the lithium metallic anode, which at present reveals the best theoretical particular electrical capability.
Now, researchers on the College of Hong Kong (HKU) have engineered solvent-free single-ion polymer electrolytes that present important enhancements in ionic transport for lithium-metal battery purposes.
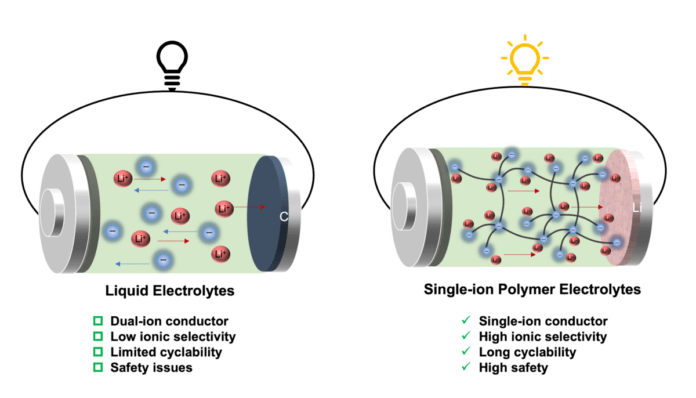
That’s, in liquid electrolytes, lithium cations and counter anions transfer in reverse instructions to conduct electrical energy. Typically, anions transfer a minimum of 4 instances quicker than lithium cations, and due to this fact the switch of lithium cations contributes solely a small half (20%) of the full ionic present. In the meantime, extra anions accumulate on the interface between the electrode and electrolyte, inflicting inner brief circuits and lack of battery capability.
New single-ion conducting polymer electrolytes designed by HKU researchers are reported to beat these limitations and result in a minimum of a fourfold improve in cationic transport.
Anionic community polymers include borate anions linked by branched ethylene glycol linkers in numerous stoichiometric ratios, the place the anions are hooked up to the polymer body, enabling a selective cation transport.
The researchers managed the cation conductivity throughout the polymer by way of the systematic engineering of segmental mobility. This helped them to map complete design guidelines for a brand new class of extremely conductive stable electrolytes, which efficiently overcome the persistent issues of current stable electrolytes, similar to low cyclability and excessive overpotential.
“We imagine that single-ion conducting polymer electrolytes will open the potential for new battery chemistries that may revolutionize the sector of rechargeable batteries, and provide a excessive stage of security, excessive energy density, and lengthy cycle in life,” stated Jingyi Gao, the primary creator of the analysis paper.
In keeping with Dr Dong-Myeong Shin of HKU, ion-selective electrolytes also can end in quick charging because of the low overpotential. “This may allow electrical autos to be totally charged within the time it takes to drink a cup of espresso. This distinctive benefit will open a brand new period in a clear vitality world,” he added.
Their findings are mentioned in “Engineered networking of a household of solvent-free single-ion conducting borate community polymer electrolytes for Li-metal battery purposes” revealed in Journal of Chemical Engineering.
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].