A analysis group from the College of New South Wales (UNSW) investigated the failure modes of heterojunction (HJT) photo voltaic modules with glass-backsheet configurations.
“We recognized 4 failure modes within the silicon heterojunction glass-backsheet module which have the potential to lead to energy lack of as much as 50% after damp warmth testing,” stated researcher Chandany Sen. pv journal. “We intention to know the doable root trigger of every failure mode and the way to detect it simply on the cell stage.”
The scientists performed their experiment on bifacial half-cut n-type silicon HJT photo voltaic cells that got here from industrial manufacturing strains of unknown producers. The merchandise are divided into three teams: modules with encapsulated cells; modules with encapsulated cell precursors; and non-encapsulated cells. For the primary two teams, the researchers used ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) encapsulant.
“All samples have an n-type wafer, intrinsic hydrogenated amorphous silicon (ia-Si:H) passivation layers on each side, and phosphorus-doped (na-Si:H) and boron-doped (pa -Si:H) hydrogenated amorphous silicon layers on the back and front sides, one after the opposite, adopted by an indium-doped tin oxide (ITO) layer deposited on each side,” they stated.
All gadgets are subjected to a humid warmth check at 85°C and 85% relative humidity (RH) for a period between 500 hours and 4000 hours.
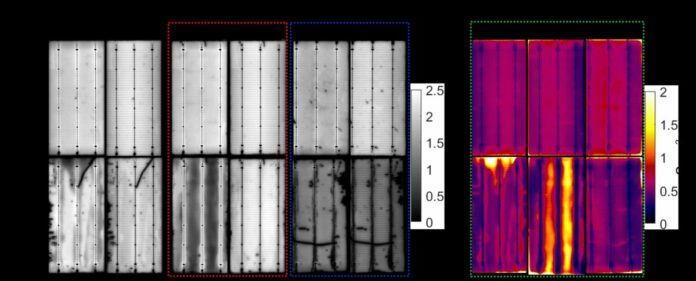
By this check, the lecturers recognized 4 failure modes for the encapsulated cells, leading to energy loss from 5% to 50%. The primary sort of failure consists of cell darkening in localized factors, and the second is represented by darkening across the interconnection of busbars and ribbon wires. The third failure mode entails extreme darkening between the interconnected areas of busbars and ribbon wires, whereas the fourth exhibits darkening of the interconnected area of busbars and ribbon wires.
Based on the group’s evaluation, the primary sort of failure is because of floor contamination, which can have occurred throughout dealing with or identification earlier than the encapsulation of the module. As for the second and third teams, scientists say that the failures are associated to the soldering flux.
“The direct impact of flux and lead (Pb) solder on inflicting contact deterioration after DH testing has additionally been noticed in different works,” they stated. “It ought to be emphasised that, in some circumstances, using a unique Ag paste additionally resulted in a Kind-3 failure.”
For the fourth group, the researchers confirmed that the failures in all probability got here from the byproduct of the EVA used for encapsulation.
“Though the experimental design of this work can not decide precisely how every failure mode occurred after the DH check, it exhibits believable conditions that may happen within the industrial setting and result in precise modes of failure noticed,” they concluded.
Sen stated that understanding and mitigating these failure modes, ideally on the photo voltaic cell stage, can be important to realizing the low value of electrical energy (LCOE) potential of the HJT. He stated that whereas glass-glass modules are sometimes used for HJT photo voltaic cells due to their lowered susceptibility to moisture ingress, related failure modes are likely to happen in these modules over longer durations of time.
The analysis group introduced its findings within the examine “4 failure modes of silicon heterojunction glass-backsheet modules,” revealed in Photo voltaic Vitality Supplies and Photo voltaic Cells.