The world takes hydrogen power storage seriously in its drive to achieve both sustainability and environmental cleanliness. The worldwide pursuit of net-zero emissions recognizes hydrogen power storage as one of its most promising answers because it achieves efficient renewable energy storage and decreases dependence on fossil fuels. An easy explanation follows to explain how this technology creates the future of clean energy.
What Is Hydrogen Power Storage?
The process of electrolysis converts renewable electricity into compressed hydrogen gas which acts as power storage through a technique called hydrogen power storage. A facility that stores hydrogen enables subsequent production of electricity and serves as motor fuel and industrial process fuel.
In short, it allows us to store energy now and use it later, which is a huge win for managing the ups and downs of renewable energy.
Why Energy Storage Matters for Net-Zero Goals
The reduction of greenhouse gas production must reach an extensive level to reach net-zero emissions. Power conservation along with cleaner energy technology must be adopted to prevent wasted clean energy. The main issue arises from renewable energy technologies which cannot produce energy when demand requires it. Both sunlight and wind power do not operate constantly throughout each day since the sun sets at night and wind speed can vary.
Storage systems built around hydrogen serve as a solution for the situation. The storage systems permit the storage of clean energy during periods of availability to utilize it during periods of peak demand or reduced supply. These systems function similarly to a substantial account which saves energy.
Why Hydrogen Over Traditional Batteries?
It’s a fair question: if batteries store energy too, why not just use them?
Batteries work well for short-term storage, especially for homes or quick energy use. But for long-term, large-scale energy storage, hydrogen offers some big advantages:
- It stores more energy for longer periods.
- It’s versatile, powering everything from homes to factories to vehicles.
- It doesn’t degrade over time the way batteries can.
- And most importantly, it’s clean—as long as it’s made from renewable electricity.
That’s why hydrogen energy storage systems are being explored for everything from city-wide power backup to fueling public transport.
How Hydrogen Power Storage Works
Here’s a quick, step-by-step look at how the process works:
1. Producing Hydrogen
When there’s more solar or wind energy than the grid can use, the extra power is used to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. This is done through electrolysis.
2. Storing the Hydrogen
Once created, the hydrogen is stored in tanks or underground facilities until it’s needed.
3. Using the Stored Energy
That stored hydrogen can be used later to:
- Generate electricity again using fuel cells or turbines
- Power hydrogen-fueled vehicles
- Run clean industrial operations
Throughout this cycle, no carbon emissions are released only water and heat. That’s a major step forward in clean energy.
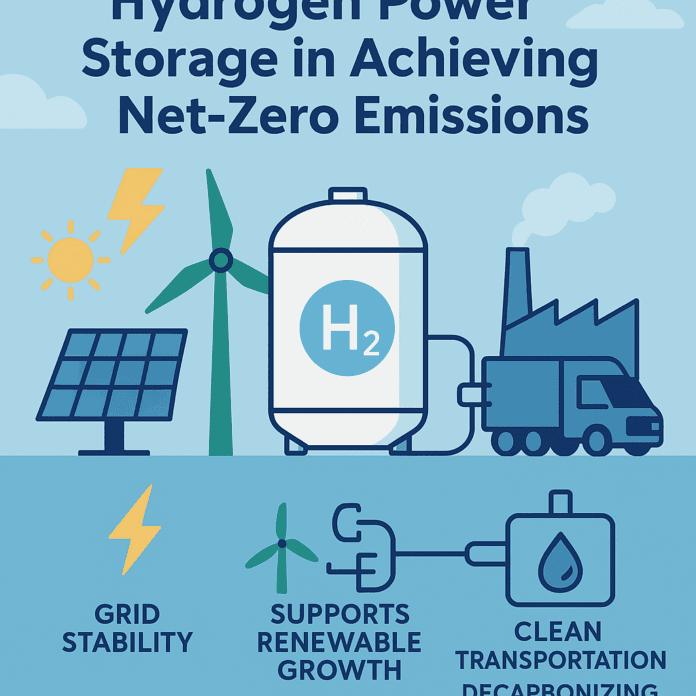
Key Benefits of Hydrogen Power Storage
Here’s how this technology supports the push toward a net-zero future:
⚡ Grid Stability
Hydrogen helps balance the electricity grid, making sure energy is available even when renewable generation is low.
????️ Supports Renewable Growth
As more wind and solar projects are developed, hydrogen storage helps capture and hold onto that power for later use.
???? Clean Transportation
Hydrogen fuel cells are already being used in buses, trucks, and trains. With reliable hydrogen power storage, cleaner public and commercial transport becomes much more realistic.
???? Decarbonizing Heavy Industries
Sectors like steel, cement, and chemicals are some of the toughest to clean up. Hydrogen offers an alternative fuel that can handle the high heat and energy demand of these industries.
What’s Holding Hydrogen Back?
While the potential is huge, there are still a few challenges to overcome:
- Cost – Right now, green hydrogen (made from renewables) is more expensive than fossil fuels, but costs are coming down.
- Infrastructure – We need more pipelines, fueling stations, and storage facilities.
- Efficiency – There’s some energy loss in converting electricity to hydrogen and back again, but ongoing improvements are making the process more efficient.
Governments and private companies around the world are investing in solutions, and progress is happening quickly.
Final Thoughts
Reaching net-zero emissions will take a mix of technologies and commitment. Among them, hydrogen power storage stands out as a key piece of the puzzle. It offers a clean, scalable way to store renewable energy and use it when it’s needed most whether that’s for powering a home, a city, or a vehicle.
As clean energy continues to grow, hydrogen energy storage systems will be critical in making sure we don’t just produce green power but that we use it smartly and efficiently, too.