As the world moves towards clean energy sources, the importance of energy storage systems (ESS) has been growing rapidly. One of the most common types of ESS is the battery energy storage system (BESS). BESS is widely used for renewable energy integration, grid stability, and electric vehicle charging. However, to ensure BESS’s safe and efficient operation, a battery management system (BMS) is essential. In this blog, we will discuss the importance of BMS in BESS.
What is BESS?
Battery energy storage systems are designed to store electrical energy for use at a later time. They are an essential component of renewable energy systems such as wind and solar power, which are variable sources of electricity. BESS can store excess energy generated during periods of low demand, or energy produce from renewable sources and release it during periods of high demand. This helps to balance the grid and maintain grid stability, which is critical for the safe and reliable operation of the electrical system.
BESS is a type of ESS that stores electrical energy in rechargeable batteries. It typically consists of multiple battery modules connected in series or parallel, a power conversion system, and a control system.
The components of a BESS typically include a battery, power conversion system, control system, and the battery management system (BMS). The battery is the heart of the BESS, storing and releasing electrical energy. The power conversion system converts the electrical energy from the battery into the desired form of output, such as AC or DC power. The control system manages the flow of energy to and from the battery, ensuring that it is charged and discharged safely and efficiently. The BMS is responsible for monitoring and controlling the battery’s performance, ensuring that it operates safely and efficiently.
BESS can be used for various applications such as peak shaving, load leveling, frequency regulation, and renewable energy integration. In recent years, the cost of battery technology has decreased significantly, making BESS an attractive option for energy storage.
What is BMS?
A battery management system (BMS) is an electronic system that monitors and controls the performance of a battery. It is responsible for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the battery, including monitoring its state of charge, temperature, and voltage. The BMS communicates with the battery’s cells, ensuring that they are charged and discharged evenly and that they are not overcharged or over-discharged. It also protects the battery from damage due to overvoltage, undervoltage, and overcurrent.
BMS is a critical component of BESS that monitors and controls the battery operation. It ensures the safe and efficient operation of the battery by managing the charging and discharging process, monitoring the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH), and protecting the battery from overcharging, over-discharging, and over-temperature. BMS typically consists of hardware and software components that work together to provide a comprehensive solution for battery management.
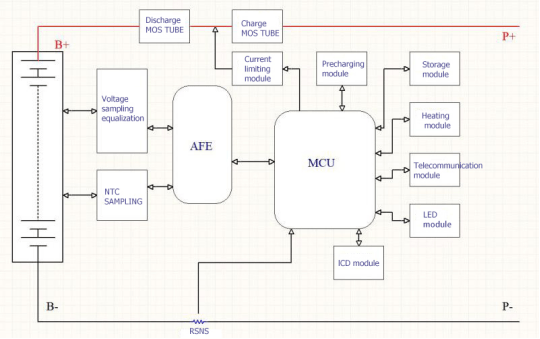
The BMS typically consists of a microcontroller, sensors, and communication interfaces. The microcontroller is the brain of the BMS, executing control algorithms and communicating with the battery’s cells. The sensors measure the battery’s state of charge, temperature, and voltage, and provide feedback to the microcontroller. The communication interfaces allow the BMS to communicate with the outside world, such as the control system or a monitoring system.
Importance of BMS in BESS:
- Safety:
Safety is one of the most critical aspects of BESS operation. Battery failure can cause severe consequences such as fire, explosion, and environmental pollution. BMS ensures the safety of BESS by monitoring the battery parameters and taking appropriate actions in case of abnormal behavior. For example, if the battery temperature exceeds the safe limit, BMS can reduce the charging rate to prevent overheating. Similarly, if the battery voltage drops below a certain threshold, BMS can disconnect the battery from the system to prevent over-discharging.
- Efficiency:
Efficiency is another important aspect of BESS operation. BMS ensures the efficient operation of BESS by optimizing the charging and discharging process. BMS uses advanced algorithms to determine the optimal charging and discharging rate based on the battery SOC and the load demand. This helps to maximize the energy storage capacity of the battery and minimize the energy loss during the charging and discharging process.
- Longevity:
Longevity is a critical factor in the economic viability of BESS. Battery replacement is expensive, and frequent replacement can significantly increase the total cost of ownership. BMS ensures the longevity of BESS by monitoring the battery SOH and taking appropriate actions to prevent battery degradation. BMS can adjust the charging and discharging rate, balance the cell voltage, and avoid deep cycling to extend the battery life.
- Monitoring and diagnostics:
BMS provides real-time monitoring and diagnostics of the battery operation. BMS can measure various battery parameters such as voltage, current, temperature, and impedance. It can also detect any anomalies in the battery behavior and alert the operator in case of any abnormality. BMS can generate reports and analytics to help the operator understand the battery performance and identify any potential issues.
- Scalability:
Scalability is an essential aspect of BESS operation. BESS can be scaled up or down depending on the energy demand. BMS provides the flexibility to add or remove battery modules from the system without affecting the overall performance. BMS can also manage the communication between the battery modules and ensure the proper functioning of the entire system.
- Integration with the grid:
Integration with the grid is an important feature of BESS. BESS can provide various grid services such as frequency regulation, voltage support, and peak shaving. BMS plays a critical role in enabling


